sureskills development process
DEVELOPMENT PROCESS OVERVIEW:
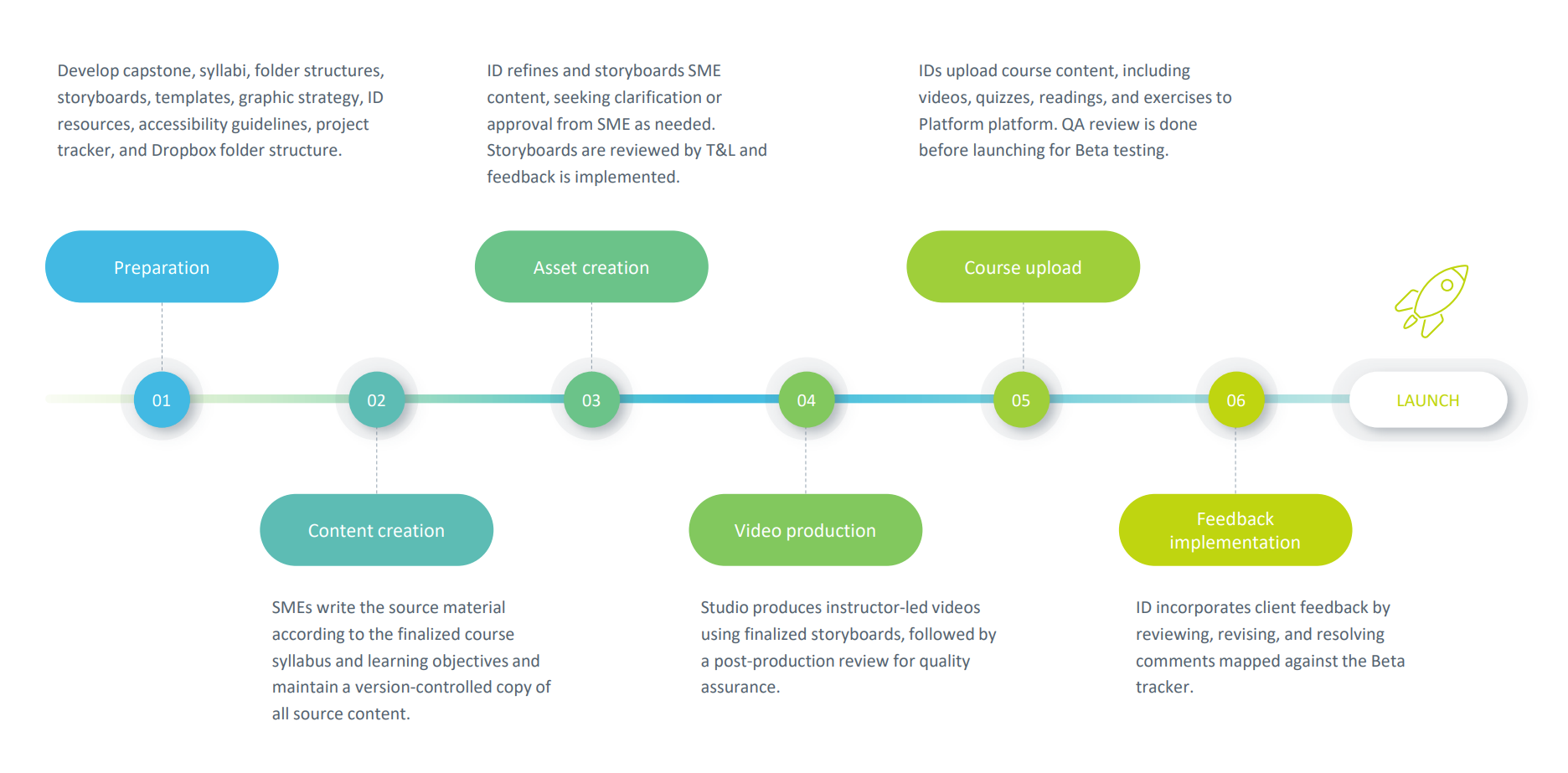

1. Preparation
The course preparation process involves developing course syllabi, creating folder structures, updating storyboards and non-video templates, preparing a graphic strategy and assets, reviewing ID resources, establishing accessibility guidelines, and creating a project tracker and folder structure.
2. Content creation
In the content creation phase, subject matter experts (SMEs) write the source material according to the course syllabus and objectives. They follow the established style guide and collaborate with instructional designers to create high-quality, engaging content.
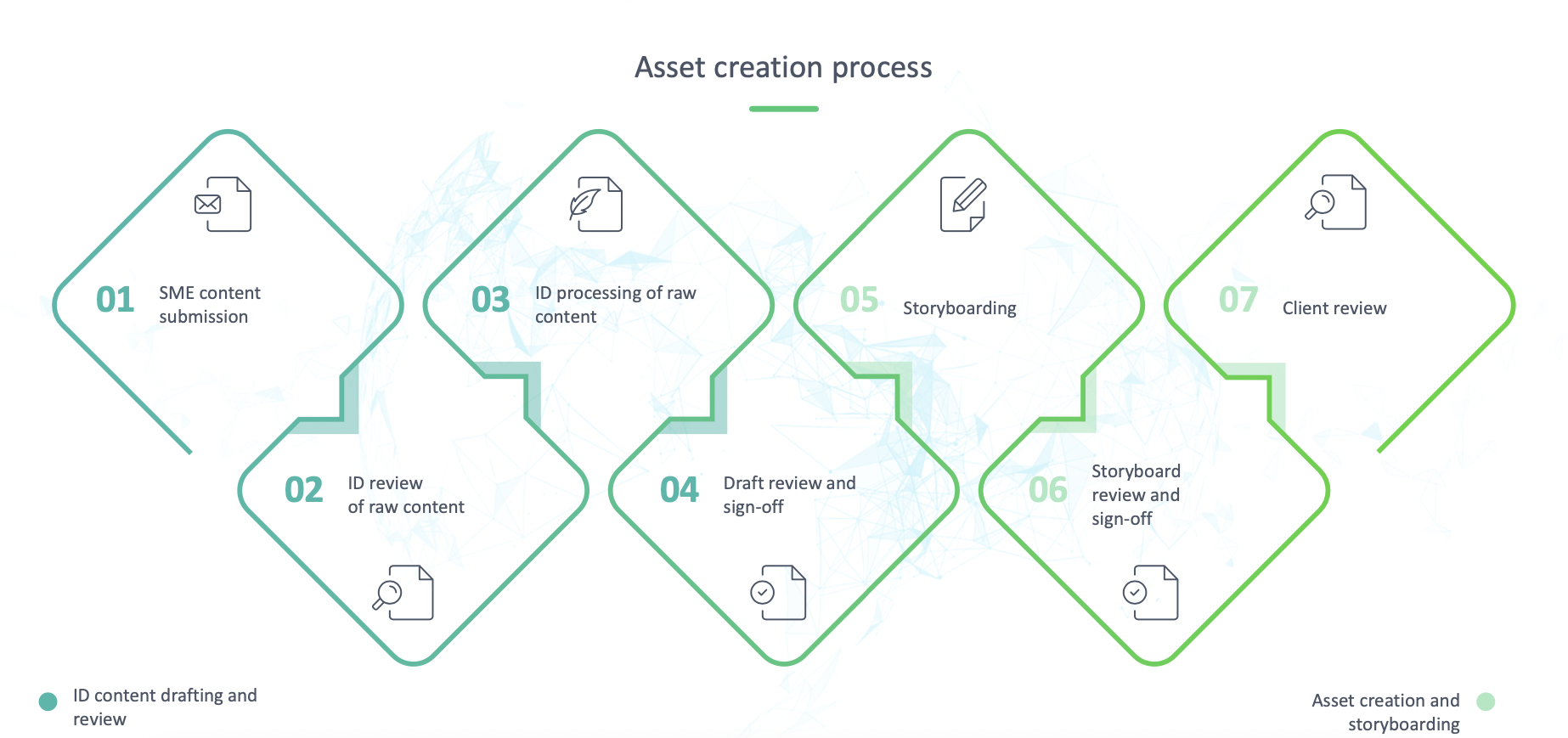
3. Asset creation
The asset creation phase includes SME content submission, ID review, processing of content, ID peer review, SME review, and sign-off. ID refines the content to meet language and structure requirements, notifies SMEs of changes, and seeks clarification or approval before storyboarding.
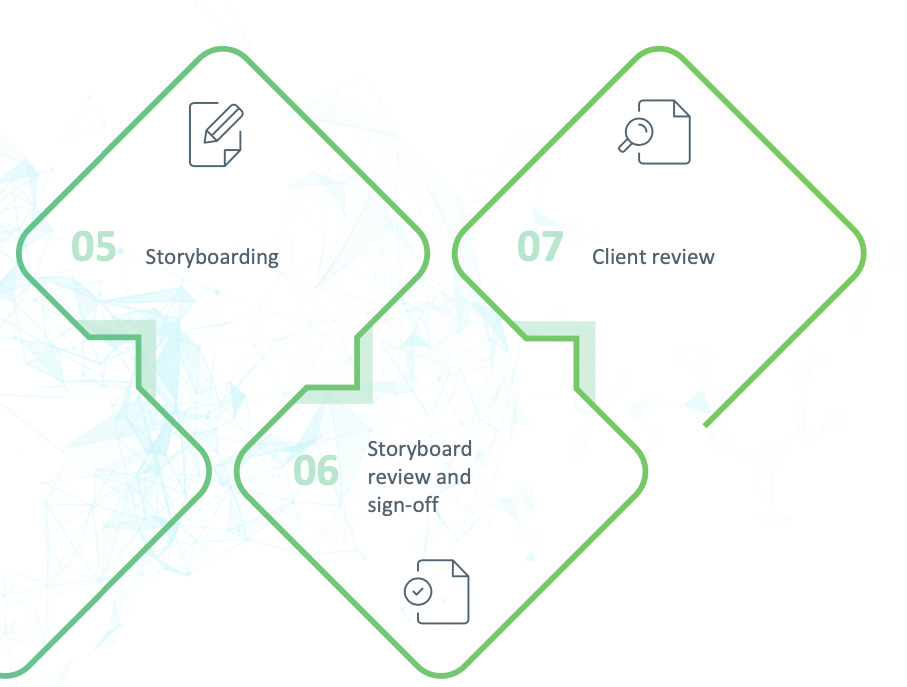
The storyboarding process involves creating a visual outline of the course content to be presented in the form of instructor-led videos. Storyboards are reviewed and finalized before going to production.
Creation and storyboarding:
Once the learning material has been signed off by SME, the content is mapped into the storyboard.
- Video items are storyboarded to include all the visuals, animations, text and VO to be used in final production.
- Non-video items are linked on the respective placeholder slides.
- One storyboard represents one lesson, and all the learning items in that lesson are mapped in the storyboard.

4. Video production:
This process involves three stages: preparation, production and post-production review. In the preparation stage, final storyboards are copied to the production folder, renamed with the PROD extension, and updated with the latest date and version number. In the production stage, videos are uploaded to Frame.io by the editors. Finally, in the post-production review stage, videos are reviewed by the ID and graphics department for further edits.
5. Course upload:
The process involves preparing a Platform course shell by requesting marketing assets, creating a course placeholder, and uploading the syllabus. Then, various components of the course, including videos, quizzes, readings, exercises, and images, are uploaded onto the Platform, with careful attention to detail to ensure accuracy and accessibility. The course undergoes platform QA and review using checklists and guidelines and is then launched for Beta testing.
6. Feedback implementation:
During the beta testing phase of a course, feedback is provided through a mapped spreadsheet. The feedback implementation process involves reviewing, revising, and resolving comments within a week. Once Beta feedback is concluded, the course is prepped for launch.

7. Launch:
Once all outstanding items are addressed and Beta feedback implemented, a final QA of the platform is performed, and the launch checklist is finalized. This includes ensuring that all graded assessments are included in the list and assigned appropriate weighting.
